Research Projects
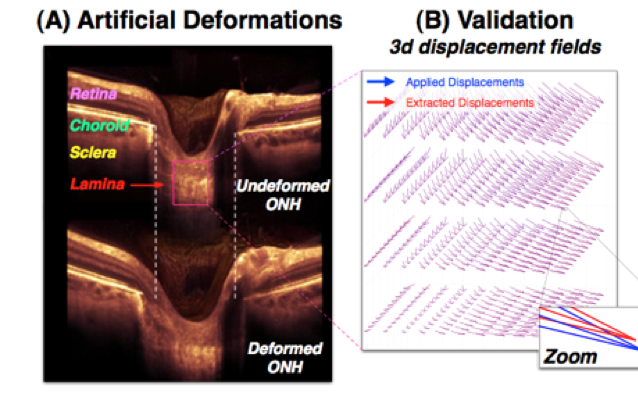
3D Deformation Mapping of the Optic Nerve Head
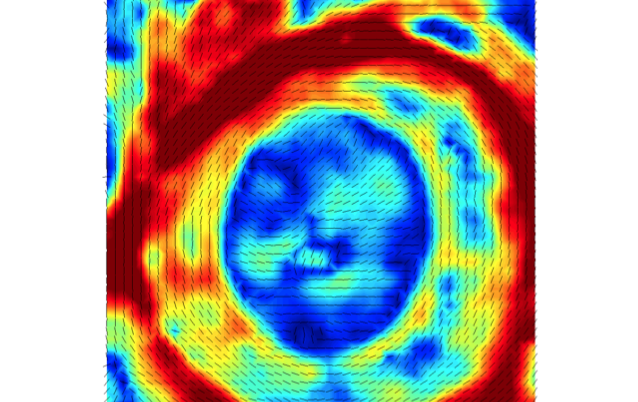
A 3D tracking algorithm has been developed to map 3D deformations of the optic nerve head in patients.
Improving Detection of the Lamina Cribrosa
Compensation techniques are used to improve the detection of the lamina cribrosa.
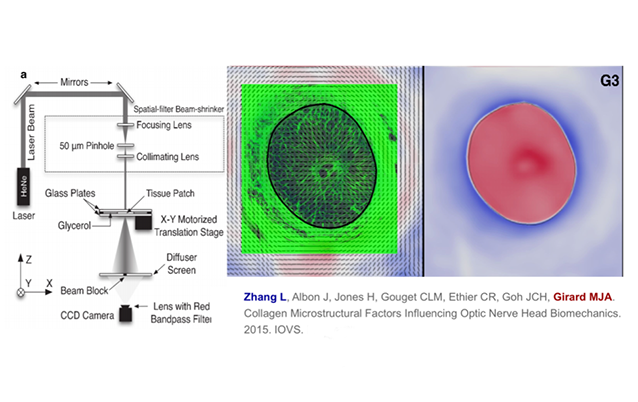
Measuring Scleral and Laminar Microstructure
Microstructure is measured using small angle light scattering.
Improving Detection of Coronary Artery Plaques
Compensation techniques are used to improve the visibility of coronary artery plaques.
Collagen Microstructural Factors Influencing Optic Nerve Head Biomechanics
Strong fiber ring in the peripapillary sclera reduced the strain level near the scleral canal.
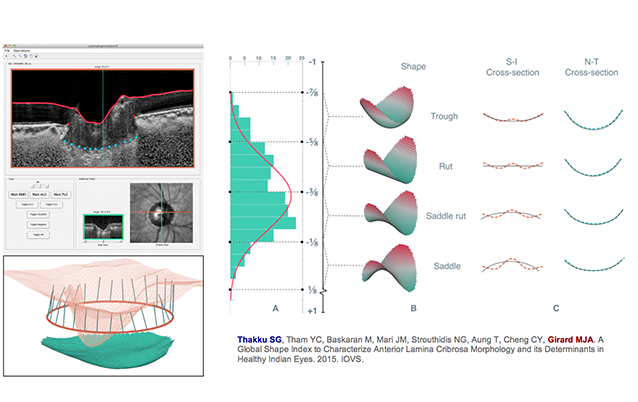
A Global Shape Index to Characterize Lamina Cribrosa Morphology
A single index that quantifies overall LC shape in an intuitive way.
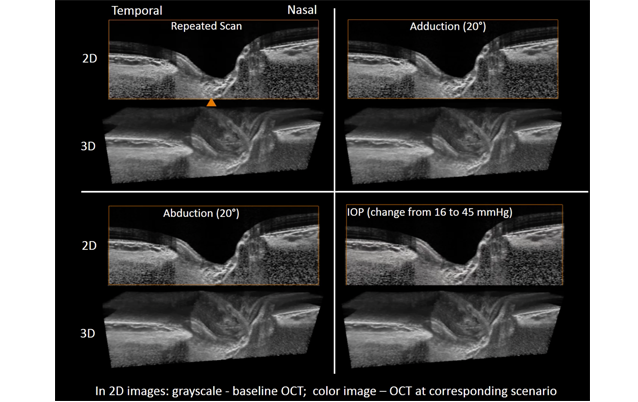
Optic Nerve Head Deformations During Eye Movement
MRI and finite element analysis have been used to predict the optic nerve head strain levels during eye movement. We found that optic nerve head deformations induced by eye movements were large. We further confirmed these large deformations using in vivo OCT imaging.